what is the inside of your elbow called
what is the inside of your elbow called – If you’ve ever pointed to that delicate inner area of your elbow while pondering its proper name, you’re not alone. Yet, despite its frequent use and vital role in arm movement, the inside of the elbow remains a mystery to many. Beyond being a cool, shaded spot on a sunny day, this area—medically termed the “antecubital fossa” or “cubital fossa”—is a core component of your elbow anatomy, intricately designed to house nerves and blood vessels essential for your arm’s function. Delve into the anatomy and significance of one of your body’s unsung heroes.
Key Takeaways
- The inside of your elbow is commonly called the “antecubital fossa” or “cubital fossa.”
- This region is crucial for the passage of important nerves and blood vessels.
- Understanding the elbow anatomy can enhance your knowledge about your body’s functionality and movements.
- The antecubital fossa plays a key role in medical procedures, such as blood draws.
- Familiarity with the terms can improve your communication with healthcare professionals regarding arm health.
Anatomical Overview of the Elbow
An in-depth understanding of the elbow joint structure is integral for comprehending how the elbow contributes to the impressive functionality of the human arm. As one of the most intricate joints in the body, the elbow plays a vital role in arm movement while maintaining stability through a versatile range of motion. what is the inside of your elbow called Let’s unpack the details of this remarkable joint, its functions, and the connective tissues that enable everything from lifting objects to performing a backhand in tennis.
The Structure of the Elbow Joint
The elbow joint structure is a harmonious assembly of bones, the humerus of the upper arm, and the forearm’s radius and ulna. This configuration allows for both a hinge action for bending and straightening and a rotational action for turning the wrist facing up or down. The crucial lattice of ligaments and muscles intertwining around these bones is essential for the stabilizing force that the elbow joint demands during various activities.
Functions and Mobility of the Elbow
The elbow’s functionality extends beyond simple bending and straightening. It enables a wide range of movements thanks to the joint’s design to rotate the forearm and position the hand. This mobility is crucial for countless daily tasks, be it typing on a computer, playing musical instruments, or engaging in sports. All these movements are made possible by the elbow’s complex structure, allowing the arm to move fluidly and effectively.
Connective Tissues and Nerves in the Elbow Area
The connective tissues of the elbow encompass an intricate network of ligaments and tendons. Ligaments connect bone to bone, establishing the joint’s stability, whereas tendons attach muscles to bones, facilitating movement. A particularly significant nerve in the elbow area is the ulnar nerve, which runs through the cubital tunnel and is responsible for the ‘funny bone’ sensation when hit. The health of these connective tissues and nerves is pivotal to maintaining elbow functionality and preventing discomfort or injury.
Naming the Parts: Understanding Your Elbow’s Anatomy
Delving into the complexity of your elbow’s anatomy reveals the precision of the human body’s design, particularly the humeral ulnar region—a key player in facilitating elbow movement.
The Humeral Ulnar Region: A Closer Look
At the junction of your arm’s humerus and ulna, the humeral ulnar region is pivotal for arm articulation. This area, which might seem obscure, is fundamental for the basic action of bending and straightening your arm. Think of this region as the epicenter of mechanical efficiency in the elbow’s anatomy.
Importance of the Elbow’s Interior in Movement
The flexibility and motion you enjoy from your forearm are due in great part to the elbow’s interior. Structures like the joint capsule and synovial membrane work harmoniously, allowing smooth movements. Whether you’re lifting a heavy object or throwing a ball, these unseen elements of your elbow’s anatomy ensure full motion range is executed with ease.
- Joint Capsule: Surrounds the elbow joint, maintaining stability while allowing necessary movements.
- Synovial Membrane: Lines the inside of the joint capsule, producing fluid that lubricates and reduces friction during elbow movement.
What Is the Inside of Your Elbow Called
When you’ve wondered about what is the inside of your elbow called, you might not have expected a term that sounds like it came out of a medical textbook. But indeed, this area has a specific and clinically significant name: the antecubital fossa. In everyday conversation, you may simply refer to it as the inside of your elbow, but in healthcare settings, recognizing this term can be quite helpful.
The antecubital fossa is more than just a channel for your blood vessels; it’s a vital structure that plays a role in the flexion and extension of the forearm. This intricacy is why healthcare professionals often utilize the median cubital vein nestled within the antecubital fossa for blood draws or IV insertions. Here’s a breakdown of the essential components you’ll find within this anatomical wonder:
| Component | Description | Clinical Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Median Cubital Vein | A superficial vein that connects the cephalic and basilic veins. | Preferred site for venipuncture. |
| Biceps Tendon | The tendon that attaches the biceps muscle to the radius. | Important for the motion of elbow and forearm. |
| Brachial Artery | Main artery of the upper arm as it continues past the antecubital fossa into the forearm. | Used for measuring blood pressure. |
| Median Nerve | Passes through the antecubital fossa under the bicipital aponeurosis into the forearm. | Can be compressed or injured, resulting in conditions such as carpal tunnel syndrome. |
The next time a healthcare practitioner mentions your antecubital fossa, you’ll understand they’re referring to a key area that holds the orchestration of nerves and vessels beneath the surface of your elbow. This knowledge not only helps in contextualizing medical discussions but also empowers you to be more attentive to the inner workings of your body.
The Role of the Cubital Fossa in Elbow Anatomy
When you delve into elbow anatomy’s interior, you’ll encounter the cubital fossa, a crucial feature often overlooked in casual conversations about joint anatomy. Yet, it’s essential to understand how this sophisticated region contributes to your arm’s functionality. The cubital fossa is not just a hollow space; it’s an intricate juncture pivotal for the mechanical and circulatory systems of your forearm.
- Neurovascular Highway: Think of the cubital fossa as a bustling intersection where vital neurovascular structures, such as nerves and blood vessels, come together. It includes the biceps tendon, the median nerve, and both the radial and ulnar arteries that supply blood further down the arm.
- Flexion and Extension: It allows for the free passage and distribution of these structures without impingement, enabling you to perform a wide range of movements from delicate tasks such as typing to more vigorous activities like lifting weights.
The anatomical significance of the cubital fossa cannot be overstated; nestled on the elbow’s interior, it plays a supportive role ensuring that flexion and extension of your arm occur seamlessly. Now, let’s break down the critical components of the cubital fossa that make up this anatomical marvel:
| Component | Function | Clinical Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Median Nerve | Transmits neural signals to the forearm and hand | Subject to compression or injury in cases of trauma to the cubital fossa |
| Biceps Brachii Tendon | Facilitates arm flexion | Can be palpated during the physical examination |
| Radial Artery | Supplies oxygenated blood to the lateral aspect of the forearm | It is a key compression point in hemorrhage control |
| Ulnar Artery | Supplies blood to the medial aspect of the forearm | Can be affected by overuse or repetitive strain |
Understanding the intricacies of your cubital fossa offers insight into how your body works in unison, orchestrating complex movements with ease and precision. So, next time you flex your arm, remember the delicate balance and the essential role this part of elbow anatomy’s interior plays in your daily life.
Common Injuries Affecting the Inside of Your Elbow
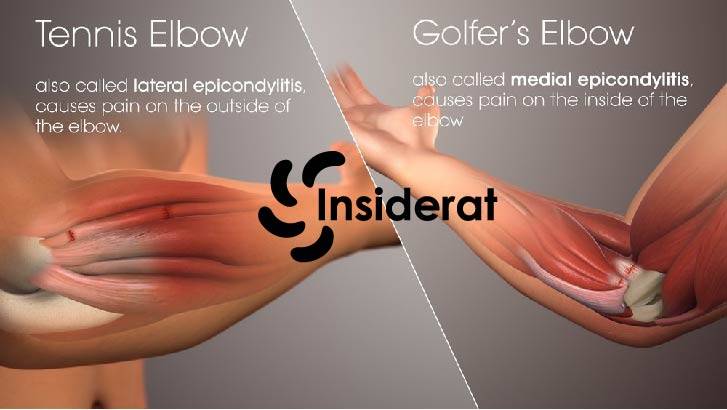
When it comes to common elbow injuries, there are several conditions you might encounter. Two particularly prevalent issues are Golfer’s Elbow, also known as medial epicondylitis, and elbow bursitis. Understanding these injuries can help you seek appropriate care and take preventive measures.
Golfer’s Elbow: Medial Epicondylitis
Golfer’s Elbow is a form of tendinitis causing pain where the tendons of your forearm muscles attach to the bony bump on the inside of your elbow. The discomfort might spread into your forearm and wrist. Repetitive stress and excessive force are often to blame for this condition, which, despite its name, doesn’t only affect golfers.
Bursitis: Inflammation Within the Elbow Joint
Elbow bursitis arises when the bursa—a small, fluid-filled sac that acts as a cushion between bones and soft tissues—becomes inflamed. It often results from repetitive motion or direct impact. Recognizable by swelling and pain, this condition can severely affect your elbow’s movement what is the inside of your elbow called.
| Condition | Common Causes | Symptoms | Typical Treatments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Golfer’s Elbow | Overuse, repetitive activity | Pain, tenderness on the inside of the elbow, stiffness, weakness in the hand and wrist | Rest, ice, compression, elevation, anti-inflammatory medications |
| Elbow Bursitis | Repetitive motion, trauma | Swelling, pain, limited range of motion | Anti-inflammatory medications, aspiration, corticosteroid injections |
If you suspect you’re dealing with either Golfer’s Elbow or elbow bursitis, it is imperative to consult with a medical professional. Early diagnosis and treatment can help avoid further complications and ensure a quicker return to your daily activities.
Medical Terminology: Beyond ‘The Inside of Your Elbow’
When navigating the complexities of elbow anatomy, it becomes crucial to understand the medical terminology that health care professionals employ. This knowledge fosters clear communication during medical consultations and helps demystify the terms related to the elbow interior. Let’s explore how these terms are not just jargon but keys to unlock a better comprehension of one’s health.
How Medical Professionals Refer to Your Elbow’s Interior
Medical experts have a lexicon that’s precise, allowing for an unequivocal description of the body’s structures and conditions. For instance, the inside region of your elbow, which houses critical veins and nerves, is often referred to as the “antecubital fossa” or “cubital fossa” in professional settings. When discussing elbow interior issues, such as pain or injury, a clinician might mention specific ligaments by name, like the “ulnar collateral ligament” or describe certain pathologies like “olecranon bursitis” to delineate the exact issues within your elbow’s intricate anatomy.
Terms You Might Hear from Your Doctor Explained
During an examination, you might encounter an array of medical terms explained with your diagnosis, which can sometimes be overwhelming. Below is a table listing common terminologies related to the elbow’s internal structures and their layperson translations, designed to aid in your understanding of medical dialogue:
| Medical Term | Description | Common Name |
|---|---|---|
| Antecubital Fossa | The interior surface of the elbow joint | Inside of the elbow |
| Olecranon Process | Bony prominence of the ulna forming the elbow tip | Elbow tip |
| Ulnar Collateral Ligament | A band of fibrous tissue that connects bones within the elbow | Elbow ligament |
| Medial Epicondylitis | Inflammation of tendons attaching to medial epicondyle of humerus | Golfer’s Elbow |
| Olecranon Bursitis | Inflammation of the fluid-filled sac at the elbow’s tip | Elbow Bursitis |
With this guide, medical terminology becomes less daunting and enhances your ability to engage in informed discussions about your elbow interior health. Don’t hesitate to ask your doctor for further medical terms explained – after all, understanding the language is the first step in comprehending the broader narrative of your well-being.
Exercises and Stretching for a Healthy Elbow
Maintaining elbow health is crucial for everyday activities that require arm movement. Introducing elbow exercises and stretching routines can be incredibly beneficial for improving the flexibility and strength of your elbow’s inner muscles. Let’s explore targeted exercises that can help safeguard your cubital area against injuries, while also enhancing your arm’s overall performance.
Stretches to Improve Flexibility of the Cubital Area
Flexibility in the cubital area not only helps with fluidity of movement but also serves as a preventive measure against elbow-related conditions. Here are some effective stretches to incorporate into your regimen:
- **Forearm Extensor Stretch** – Extend one arm in front of you with your palm facing down. Use your other hand to gently press down on the fingers, stretching the upper side of your forearm.
- **Forearm Flexor Stretch** – With your arm extended and palm facing upwards, draw back your hand toward your body using the other hand to enhance the stretch in your forearm’s inner muscles.
Consistently practicing these stretches can lead to increased flexibility in the cubital area, contributing to a healthier range of motion.
Tips for Strengthening Your Elbow’s Inner Muscles
Strengthening the muscles surrounding the elbow joint provides better support and reduces the risk of strain. Incorporate these elbow muscle-strengthening exercises into your routine:
- **Elbow Flexion and Extension** – Using a lightweight, sit with your arm rested on your thigh. Slowly bend your elbow to bring the weight toward your shoulder, then extend your arm out straight.
- **Wrist Curls** – Support your forearm on a table with your wrist and hand extending off the edge. Holding a weight, curl your wrist up and down to work the muscles in your forearm.
Regular execution of these exercises will not only fortify the muscles in your elbow’s interior but will also boost overall elbow stability and function. Remember, patience and consistency are key to seeing results and preventing injuries.
Understanding Your Elbow’s Inside: FAQs
Understanding your elbow involves more than just recognizing its location on your arm. It’s about knowing how this complex joint works, the issues that can affect it, and how to care for it. In this section, we’ll delve into some common elbow FAQs to enlighten and inform you about the inner workings of your elbow.
- What structures are located inside my elbow?
- The inside of your elbow, or antecubital fossa, contains several crucial structures including tendons, nerves, muscles, and blood vessels.
- How does the elbow’s interior affect arm movement?
- The range of motion and stability of your arm is heavily reliant on the elbow’s interior structures working in harmony. Flexion and extension of the arm are primarily facilitated by this intricate area.
- What are common conditions that affect the inside of the elbow?
- Conditions like medial epicondylitis (Golfer’s Elbow) and bursitis commonly afflict the inside of the elbow, leading to pain and reduced mobility.
- Can exercises help maintain the health of my elbow? Yes, exercises and stretches specifically designed for the elbow’s interior structures can help maintain joint health, prevent injuries, and enhance overall arm strength and flexibility.
- What should I do if I experience pain inside my elbow?
- Consult a healthcare professional if you experience elbow pain. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent more severe problems in the future.
If you have more questions or want to deepen your understanding of your elbow, consult with medical professionals who can provide personalized advice and care.
Conclusion
In summarizing elbow anatomy, we’ve explored the complexity and the extraordinary capabilities of one of your body’s remarkable joints. Understanding the inside of your elbow, called the antecubital fossa, is not just a matter of simple curiosity. It’s a dive into the gateway that houses critical veins, arteries, nerves, and muscles crucial for arm and hand functions. This knowledge not only feeds your intellectual interests but also lays the groundwork for maintaining proper arm health and preventing injuries.
Your arm’s dexterity and range of motion rely heavily on the health and integrity of this area. The antecubital fossa, in concert with the surrounding skeletal and soft tissue structures, facilitates a wide range of movements—from the precise action of writing to the dynamic throw of a ball. By demystifying how it accomplishes these tasks, you gain more than insight; you also receive the motivation to care for this vital region through appropriate stretches and exercises.
As we close this discussion, it’s essential to remember that the elbow is more than just a hinge; it’s a complex system crucial for countless daily tasks. So, the next time you bend your arm, consider the remarkable anatomy at work, particularly the role of the inside of your elbow, and perhaps look at it with a newfound sense of appreciation and understanding.
FAQ
What is the inside of your elbow called?
The inside of your elbow is commonly known as the “antecubital fossa” or “cubital fossa.” It is a triangular area that provides a passage for nerves and blood vessels.
Can you provide an anatomical overview of the elbow?
The elbow joint is a complex structure that includes the humerus, radius, and ulna bones. It is supported by ligaments and muscles that provide stability and flexibility. The elbow enables bending, straightening, and rotating motions of the forearm.
What are the connective tissues and nerves involved in the elbow area?
The elbow area contains several important connective tissues such as ligaments, tendons, and a joint capsule. The ulnar nerve is a major nerve that runs through the cubital tunnel in the elbow and is responsible for sensation in the hand.
Why is the elbow’s interior important in movement?
The elbow’s interior includes the joint capsule and synovial membrane which contribute to the elbow’s range of motion. This allows for daily activities that involve lifting, reaching, and throwing.
What is the role of the cubital fossa in elbow anatomy?
The cubital fossa is crucial as it houses vital neurovascular structures such as the radial and ulnar arteries, and veins like the median cubital vein, which are essential for blood supply to the forearm and hand.
What are some common injuries affecting the inside of your elbow?
Common injuries include Golfer’s Elbow, or medial epicondylitis, which is a form of tendinitis, and elbow bursitis, which is the inflammation of the bursal sac due to repetitive motion or trauma.
How do medical professionals refer to the inside of your elbow?
Medical professionals often use terms like “antecubital fossa,” “cubital fossa,” or “medial epicondyle” when referring to the inside of your elbow, depending on the context and specific area they are addressing.
What stretches can improve the flexibility of the cubital area?
Stretches that extend and flex the forearm muscles can improve flexibility in the cubital area, such as wrist flexor stretches and elbow extensor stretches.
Are there exercises that specifically strengthen the elbow’s inner muscles?
Yes, exercises like wrist curls, reverse wrist curls, and forearm pronation/supination can help strengthen the muscles around the elbow’s inner part, providing better support to the joint.